
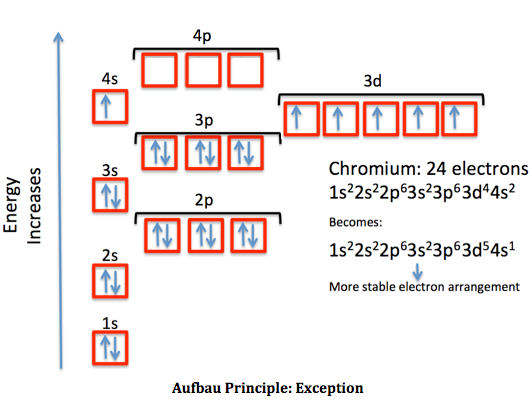

The Pauli exclusion principle in advanced physics is one of the most basic observations of nature. Pauli’s exclusion principle has an integral part in atom physics because the arrangement of electrons is one of the significant parts of the atomic structures. These are some of the examples that show how Pauli’s exclusion principle is used. Later if we ruminate the Pauli exclusion principle, if there are two electrons in a state, then all of the electrons will spin up or spin down-state but not similar. If the state has one electron, then it can also be spin-up or spin down. Mostly it is asked how does the principle work or where does it can be applied? If we look at the atoms every time it advances a new electron or electrons it ordinarily changes to the lowest energy state or it moves to the outermost shell. In chemistry, the law is essentially used to elucidate or define the electron shell structure of atoms and forecast which atoms are probable to donate electrons. He was even chosen by Albert Einstein to be awarded. Wolfgang Pauli has presented the Nobel prize in the year 1945 for the detection of the Pauli exclusion principle and his complete contribution in the field of quantum mechanics. Whereas Bosons get their name from the Bose-Einstein distribution purpose. The nomenclature goes, fermions are named after the Fermi–Dirac statistical dissemination that they follow. Furthermore, bosons can share or consume the same quantum states, distinct from fermions. It is not related to particles with an integer spin such as bosons which have symmetric wave purposes. It relates to other particles of half-integer spin-like fermions. Though, the Pauli Exclusion Principle does not only relate to electrons. The two electrons that occur in a similar orbital should have opposite spins or must be antiparallel.Only two electrons can conquer a similar orbital.There are two relevant procedures that the Pauli Exclusion Principle follows: To explain it more simply, each electron must have or be in its own unique state. The Pauli exclusion principle states that in a single atom no two electrons will have a matching set or equal quantum numbers (n, l, ml, and ms).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
